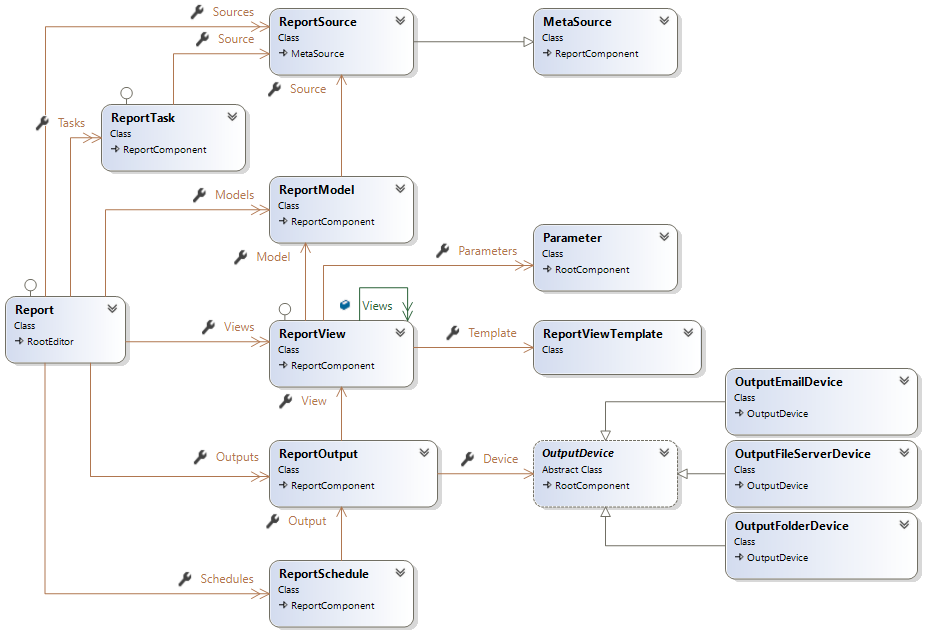
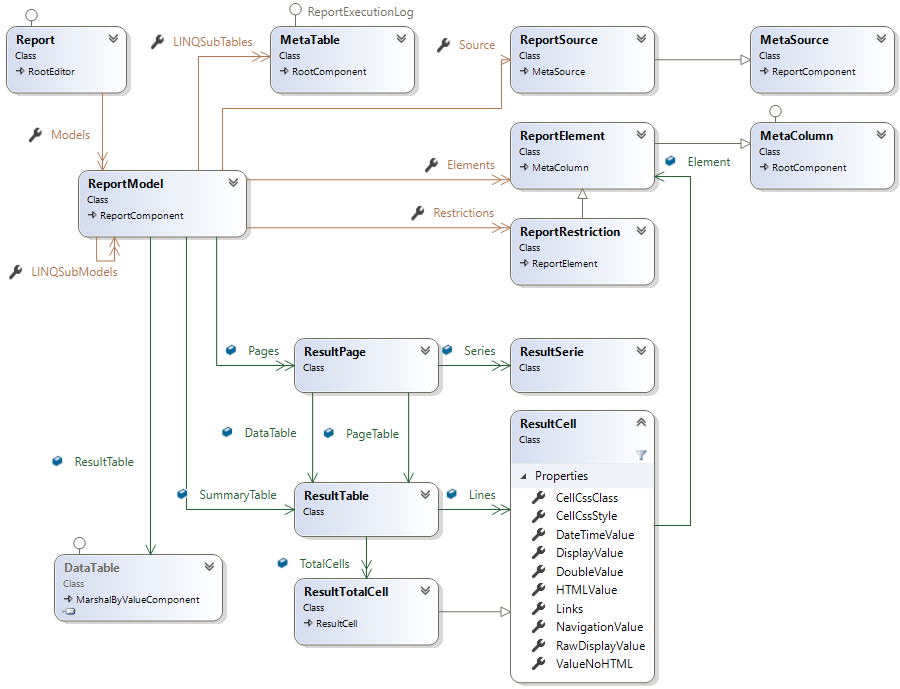
Reports
A Report is edited with the Report Designer and stored in a file (*.srex) either in the \Reports Repository sub-folder or on the file system.
A report references repository Data Sources but it may have its own Data Sources definitions.
A report contains Models to define how to generate the Result Set (Data Table) and Series from the database.
Once the result got from the database (for SQL Source) or from script (for LINQ Source), report Views are used to generate a HTML document using Razor parsing and rendering.
In addition, Outputs and Schedules can be defined to automate report generation (
Report allows also to perform Tasks to execute SQL or Razor Scripts.
Models
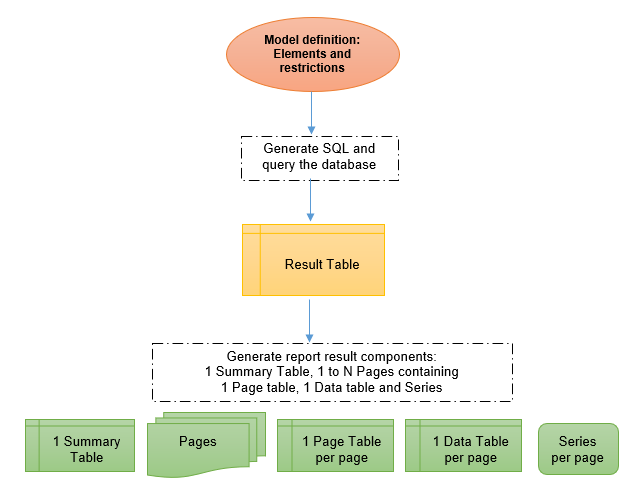
A Model defines how to build the SQL Select or the LINQ Query Statement to get the result set from the database.
A report can contain several models referencing different data sources (one data source per model).
Once got from the database or from the LINQ query, the result set is processed in a Summary Table and several Pages containing a Page Table, a Data Table and Series if a chart is defined.
The Data Source chosen defines which elements and restrictions are available to define the model.
Model Definition
Once the Source defined, the Connection can also be chosen for the model.
Several scripts allow to modify the model before or after the table is loaded and processed: Pre Load Script, Post Load Script, Final Script.
You can also override the default SQL generated with the following properties :
Select Clause,From Clause,Order By Clause,Group By Clause,Common Table Expression Clause
As a model can depend on other model generation (Load Scripts, but you want to be sure that is has been executedExecution set property allows to define when the model is generated during the report execution.
Samples
In MS MSQLServer, set theSelect Clause to SELECT TOP 100 to limit the result to 100 records.Add a custom restriction in the
From Clause to enhance your SQL performances.Add a column in the
Order By Clause to sort the result on a column not shown in the report.
Like tables in Data Source, Pre/Post SQL Statements can be executed just before and after the SELECT statement is executed.
Finally ,the model definition allows to configure build timeout and join preferences, and to edit all the Common Restrictions found in the SQL generated for the model (use the property Common Restrictions).
Elements
The Data Source chosen for the model defines the elements available
You can drag and drop the elements you want to see in your report in four different panels corresponding to a cross table definition:
Row/Column for the dimensions of the result table, Data for the measures aggregated and Page to force a new page per page value.
Once chosen, the element can have a custom Name, and Sort order.
The sort priority is the following: First Page elements, then Row/Column elements and finally Data elements.
In addition, the element Data type and Format can be modified to change the display result.
Properties for Data element
-
Aggregateto choose which aggregation will be done: Sum, Average, Count, Min, Max. -
Calculation optionto change the display in % of the row, column or total. -
Totalsto add extra line or column containing the total of the other cells in the result table.
Advanced Properties
-
Custom SQLto change the default SQL used for the element (which comes from the column name).
By changing the SQL, you can use all SQL functions/operators/features supported by the database engine or other column of the table. Thus, formula can be defined at this level. Once modified, be sure that the new SQL generated is still correct (F8).
-
Cell scriptto execute a razor script when the table cell is generated.
The script can modify cell presentation and value (e.g. Setting the font color in red if the value is negative, calculating a progression or a running total, etc. ).
Using cell scripts can be time consuming as the script is executed for each cell of the tables generated. -
Custom enumerated listto force an existing enumerated list to use its display and sort.
Custom SQL Samples
Replace Orders.Amount by 2*Orders.Amount to multiply your measure by 2.Replace Orders.Amount by Orders.Amount/Orders.Quantity to get a unit price.
Change Country by a CASE WHEN Country='France' THEN 'Other' ELSE Country END Clause to categorize your countries.
Cell script
Live Sample: 05-Scripts/501-Cell Script - Progression and running totalsTwo columns have been added in the report model with custom Cell script: One to calculate the Progression and the other one to calculate the Running Total.
Sharing elements and restrictions amongst models
If your report contains several models having the same elements or restrictions, you can configure one model and reference it from the other models using theReference model property.Live Sample: 14-Sharing Models and Views properties
Restrictions
Restrictions are used to filter data displayed in the report result
You can drag and drop the elements into the Restrictions text or into the Aggregate Restrictions text to add the restriction to the model.
The Restrictions text is then used in the SQL WHERE Clause and the Aggregate Restrictions text in the SQL HAVING Clause.
SELECT Country,SUM(Amount) FROM Orders
WHERE Country='France'
GROUP BY Country
HAVING SUM(Amount)>10)
A restriction inherits from an element, thus several properties are common: Name, Data type, Custom SQL, Custom enumerated list.
The operators available for the Operator property depend on the element type (Text, Numeric or Date & Time).
Date & Time keywords
If the restriction is a Date & Time, keywords can be used to have value relative to the execution date time: Now, Today for the current day, ThisMonth for the first day of the current month, etc.
In addition to the keyword, the value can be changed by +/- operations with a given unit (s for seconds, m for minutes, h for hours, D for Days, W for Weeks, M for Months, Q for Quarters, S for Semesters, Y for Years)
Keywords Samples
'Today - 1D' is yesterday'ThisMonth +1M - 1D' is the end of the current month
'ThisQuarter +1Q - 1D' is the end of the current quarter
'Now+1.5s -2m +3h' gives the current time plus 1.5 seconds, minus 2 minutes and plus 3 hours...
Prompting the value at execution
When the report is executed, the restriction value can be prompted to end-user by modifying the Prompt Restriction property.
In this case, the properties Trigger execution, Is Required and Operator style can be set.
If the restriction has an Enumerated List, other properties allow to control its display layout (Enum Layout) and the values selected the first time (First selection).
Sharing prompted restrictions amongst models
If several restrictions have the same display name and the same metadata source column, only one restriction will be prompted (the one with the lowest display order) and the values will be dispatched to all model restrictions.This is also applied for Common Restrictions (but only the name is used as common restriction does not have source column).
Another method to share restrictions is demontrated in the report:
Live Sample: 14-Sharing Models and Views properties
Flags 'Value only'
If the Operator is 'Value Only', the SQL generated for the restriction will not include the column name and operator and set only the value.
Operator is set to 'Value only', the name of the operator is taken from Operator label and the SQL generated is 'France'Reference model
If your report contains several models sharing the same elements or restrictions, you can configure one model and reference it from the other models using theReference model property.If set, restrictions and elements from the referenced model are inserted to the current model. This enables the sharing of restrictions and elements among different models.
The position of the element inserted can be specified in the
Insert position element property in the referenced model.Live Sample: 14-Sharing Models and Views properties
Charts
Charts axis and series are also defined in the report model.
Three JavaScript Chart libraries are supported by Seal Report: Chart JS, NVD3 Chart and Plotly Chart.
A Chart library to generate static images is also available: ScottPlot Chart.
According to the library chosen, the look and functionalities are different but we recommand to use Chart JS first (for maintenance and performances reasons).
The ScottPlot Chart library can be used to get the best rendering for the PDF format.
Serie Definition property to Axis, then select a Data element and define the serie with Chart JS serie or NVD3 serie or Plotly serie.
Instead of being an axis, a dimension can be a Splitter to create several series when the value changes (
For Date & Time or Numeric axis element, if the flag Use value for axis is true, the values of the dimension element is used to build the axis values, otherwise the X values are linear.
Other properties allow to control Sort type and Sort order of the chart (Y Axis Type (
Charts with No Axis
It is also possible to define a chart without axis.In this case the name of the data elements are used to build a single serie with an axis and their values (
Charts Samples
Live Sample: 04-Charts Gallery - Basics Live Sample: 05-Charts Gallery - AdvancedThese two reports show different chart definitions with their renderings using the three supported libraries. Live Sample: 04-Charts Gallery - Chart JS Labels
This report shows how to use the Chart JS Labels.
Live Sample: 05-Gauges Live Sample: 20-KPI
To show the use of Gauges and Key Performances Indicators (KPI).
SQL Model
A SQL Model is a report model defined with a simple SQL Select Statement edited by the user designing the report.
It is equivalent to creating a table with dynamic columns in the Data Source with a simplified edition.
When the SQL Select Statement is modified, the elements available are updated.
The option Use raw SQL indicates to use directly the SQL Select Statement to generate the result table instead of using a 'select * from (SQL Select Statement) a' statement.
In this case, aggregations, restrictions and custom SQL cannot be used.
Note that the SQL Select Statement may contain Common Restrictions.
Converting a model
A SQL Model cannot not have join to other tables defined in the Data Source, however you can convert a SQL Model to a normal MetaData Model.In this case, a new table is create in the Data Source and the model elements refer to this new table.
You can also convert a MetaData Model to a SQL Model, the SQL generated for the model will be then used for the SQL Select Statement. This may be useful to customize the SELECT generated for a report.
Just right click on your model in the TreeView to show the conversion popup menu.
SQL Model Sample
Live Sample: 08-SQL Model - Common RestrictionsThis report shows a simple SQL Model based on the query of the Northwind database sample.
A Common Restriction and a Common Value are defined in the SQL and prompted at execution.
LINQ Model
A LINQ Model is a model based on a LINQ Data Source.
It is managed as a normal model except that the Seal engine will generate a LINQ Query instead of an SQL Statement to get the result table.
For each model, the engine will generate 0 to many Sub-Models and 0 to many Sub-Tables.
One Sub-Model is created for each SQL Data Source involved (by an element or a restriction part of the model).
One Sub-Table is created for each No SQL Table involved (by an element or a restriction part of the model).
These Sub-Models are models referencing a SQL Data Source and can be edited as normal models (
The Sub-Tables properties may also be edited and customized.
The LINQ Load Script and LINQ Query Script template properties of the model allow to customize the query generated by the engine.
Elements and restrictions of the model can also have a Custom expression to overwrite the default expression generated (
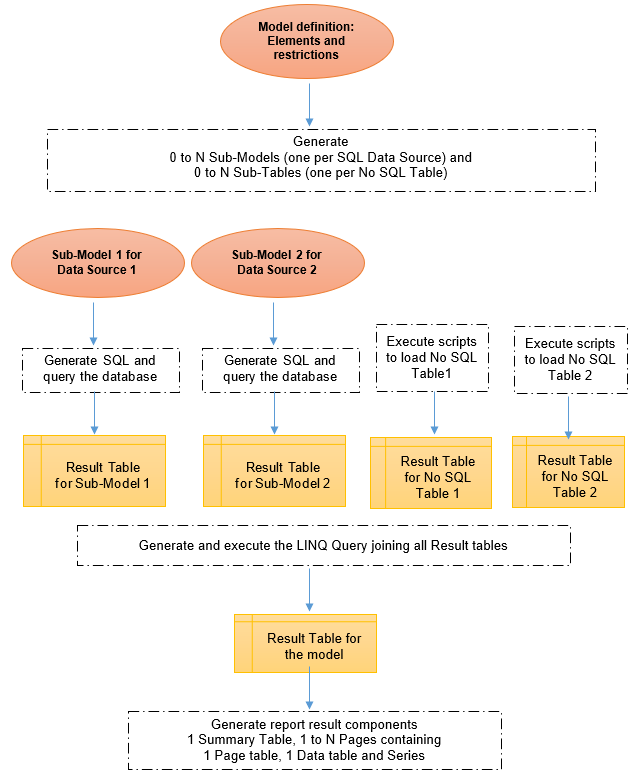
In the LINQ Query, elements defined in a No SQL table are named with the Table Name and the Column Name (
LINQ Query Sample
This script is generated for theExcel Employees Objectives model of the report:Live Sample: 02-LINQ/201-LINQ Samples CSV-Excel-JSON-XML
@using System.Data
@{
ReportModel model = Model;
//Query
var query =
from Northwind in model.ExecResultTables["Northwind"].AsEnumerable()
join ExcelEmployeeObjective in model.ExecResultTables["ExcelEmployeeObjective"].AsEnumerable() on
new {x1=Helper.ToString(Northwind["Employees.LastName"]), x2=((DateTime)Northwind["DATETIME2FROMPARTS(year(Orders.OrderDate),1,1,0,0,0,0,0)"]).Year}
equals
new {x1=Helper.ToString(ExcelEmployeeObjective["employee"]), x2=Int32.Parse(ExcelEmployeeObjective["year"].ToString()) }
group new { Northwind,ExcelEmployeeObjective } by new {
C0=Helper.ToDateTime(Northwind["DATETIME2FROMPARTS(year(Orders.OrderDate),1,1,0,0,0,0,0)"]),
C1=Helper.ToString(Northwind["Employees.LastName"]),
C4=Helper.ToDouble(Northwind["Employees.EmployeeID"])
} into g
orderby g.Key.C0,g.Key.C1,g.Sum(i => Helper.ToDouble(i.Northwind["(1-[Order Details].Discount)*[Order Details].Quantity*[Order Details].UnitPrice"])),g.Sum(i => Helper.ToDouble(i.ExcelEmployeeObjective["objective"]))
select new {
C0=g.Key.C0,
C1=g.Key.C1,
C2=g.Sum(i => Helper.ToDouble(i.Northwind["(1-[Order Details].Discount)*[Order Details].Quantity*[Order Details].UnitPrice"])),
C3=g.Sum(i => Helper.ToDouble(i.ExcelEmployeeObjective["objective"])),
C4=g.Key.C4
};
//LINQ Query Script
var query2 = query.Distinct();
model.ResultTable = query2.CopyToDataTable2();
}
Report Restrictions in LINQ
Restrictions are shared amongst the LINQ Model and its Sub-Models.For performance reasons, it is recommended to set the restrictions in the Sub-Models of the LINQ Model, thus the database engine will perform the filter on the result set.
Views
Views are used to generate the report result from the models results.
A view is implemented as a Razor script that will be compiled and executed when rendering the report.
A view references a View Template. The template defines the default razor script and the view parameters.
The script and the parameters can be customized per view.
To be executed, a report has at least a root view referencing the Report Template.
A view can have children views, the rendering starts from the root view and ends at the last child views (from top to bottom).
After the execution of the view, the HTML or the text generated is appended to the report result.
A view has several parameters to change the rendering (
The parameters are defined in the view template configuration file. They may have different purposes and depends on the components/items handled by the view.
Model Views
Certain views reference a model, in the case the rendering is done using the model results.
When executed, a report model has a report model result: one summary table and several result pages. Each page has a Page Table, a Data Table and Chart Series.
Thus , there are dedicated views to render these results.
Customize your rendering
If necessary, the view scripts can be customized to get the rendering you want.Set the
Use custom template flag to true and edit the Custom template property.If the view has Partial Templates, you can modify them using the
Custom Partial Templates collection.
Templates
All View Templates are defined in .cshtml files located in the \Views Repository sub-folder.
Here is the list of the current view templates supported:
- Report: Root view containing all the code necessary for the report execution.
- Model: Main view to display a model. Its children are dedicated to view each part of the model result: Page tables, Data tables, Charts, KPI.
- Model Detail: Show a model as a detailed record. This view works for a model result having a single record.
- Container: A Boostrap layout container (refer to Bootstrap 3 grid at https://getbootstrap.com/docs/3.4/css/#grid).
- Container Grid Flex: A Grid or Flex layout container (refer to CSS references at https://getbootstrap.com/docs/3.4/css/#grid).
- Card: A view to display each model values in a single card.
- Widget: A container to display a panel with a title, icon and color. A optional report can be executed from the title.
- Tab Control: A Tab Control container. Only Tab Page children can be defined from this view.
- Tab Page: Container for a given page of the parent Tab Control. The name of the view is used for the Tab.
- Free: Empty view that can be used freely to add HTML or text during the rendering.
- Restrictions: Render some selected report restrictions (named View Restrictions) to display model Views dynamically through restriction Triggers or a Refresh button (refer to Restriction Views).
From a Model view, the following children are supported and are applied per page result:
- Page Table: Render the Page table of the page result.
- Data Table: Render the Data table of the page result (use of the DataTables JavaScript Component).
- Chart JS: Render the Chart JS series of the page result
- NVD3 Chart: Render the NVD3 series of the page result
- Plotly Chart: Render the Plotly series of the page result
- KPI: Display a Key Performance Indicator. The KPI is built from a data table result with at least 2 columns: 1 for the dimension, 1 for the measure (with optional columns to define the goal if the column name has the _GOAL suffix).
- Gauge: Display a Gauge built from a data table result having at least 1 row and 1 column for the value. 3 optionals columns can be used to set minimum, maximum and animation speed.
Data Tables: Server Pagination
By default and for performances reason, tables are displayed using server pagination, this means that the cell values of a page are sent to the browser when the user click on a page number. (For a report, the server pagination can be enabled or disabled using the root view parameter and the model view
Options: Server pagination enabled.
Report Formatto choose the result format: HTML, CSV, HTML Print, Excel, PDFDisplay: Execution Messagesto control the messages panel of the report result. Use Messages enabled and shown for a report having only tasks.Display: Restrictions per rowto configure how many prompted restrictions are displayed per row.Options: Force Executionto execute the report even if a restriction is prompted.Options: Auto-Refreshto re-execute automatically the reports every xx seconds.
Options: Invert data tableto swap the columns and rows of the data table from their original presentation. This is valid only if the server pagination parameter is disabled in the root view and in the related model view.Options: Columns to hideto hide columns in the table (e.g. the column is only used for a sort or for a calculation ).
Reference view
If your report contains several views sharing the same configuration, you can configure one view and reference it from the other views using theReference view property.Live Sample: 14-Sharing Models and Views properties
Create your own View Template
It is easy to create your own view templates.Just add two *.cshtml files in the \Views Repository sub-folder: one for the main script and one for the configuration.
Renderers
In addition to the default HTML renderer, a view has multiple renderers to generate the report result in various formats.
Like a view, a renderer has also a Renderer Template defined in .cshtml files located in the \Views\Renderers Repository sub-folder.
These templates can be easily customized either in their file definition or within the report itself.
The following renderers are implemented:
- CSV: Generates a CSV file.
- Excel: Generate an XLSX file using the EPPLus library.
- HTML to PDF: Generate a PDF from the HTML Print format using the PuppeteerSharp library.
- Json: Generate a simple Json file.
- PDF: Generate a PDF file using the PDFQuest library and PuppeteerSharp library if JavaScript Charts or Gauge are involved.
- Text: Generate a simple text file.
- XML: Generate a simple XML file.
Excel and PDF samples
Live Sample: Renderer Excel - OrdersThis report extracts orders and details in an Excel sheet.
Live Sample: Renderer PDF - Invoice
This report generates an invoice in PDF ready to print.
Restriction Views
By default, all prompted restrictions are displayed in a panel located at the top of the report.
Using a Restriction View allows to show them in any part of the report result.
Once the restriction triggered or the Refresh button pressed, the model views impacted by the new restriction value are updated in the report result.
The Restrictions property allow to choose the prompted restrictions involved in the view.
If one of the restrictions of the view has the Trigger execution flag set to False, a Refresh button is also displayed to allow the execution.
If the property Target window is set, the execution occurs in a new window using the optional view defined in Target window: View to execute.
Samples
Live Sample: 31-Restrictions ViewsThis report shows different ways to use Restriction Views in a report result.
Outputs and Schedules
A Report Output defines how to generate the report result of a root View to an Output Device (Folder, File Server or Email).
A report can have several outputs on different devices.
The execution of an output can differs from the normal report execution in several ways:
Custom restrictions to specialize the restriction values of the report.
Custom view parameters to change the parameter values of the root view (
Culture to change the culture (
Conditional generation
If Cancel generation if no records is set to true, the output generation is cancelled if the result set has no records.
Pre/Post-generation scripts can be defined and executed before and after the generation.
The Pre-generation script allows also to cancel the output generation when more complex conditions are met.
Security
As an output can be scheduled and executed by the Task Scheduler, you can define particular security context using the User name and User Groups properties.
In this case, the user name and groups are used to execute the output. This may be useful if you have defined dynamic security based on user name or groups.
Devices
A Device is used to define a Report Output.
The following types of devices are supported:
-
Folder: To generate the report result into a file on the file system.
The Folder device is always available. -
File Server: To generate the report result into a remote directory of a file server.
File Server devices are edited and configured using the Server Manager and are stored in a file (*.scfx) in the \Devices\FileServer Repository sub-folder.
The following protocols are supported: FTP, FTPS, SFTP, SCP. -
Email: To send the report result by email through a SMTP server.
Email devices are edited and configured using the Server Manager and are stored in a file (*.scfx) in the \Devices\EMail Repository sub-folder.
The configuration contains all parameters required to send an email through a SMTP server.
Used for notification set to true to allow schedule notifications.
Schedules
A Schedule is a regular execution of a report output.
A report output can have several schedules.
Several properties allow the configuration of the notifications and fail-over procedures (
Windows Task Scheduler
By default on Windows OS, the execution is done through the standard Windows Task Scheduler via the batch executable Task Scheduler located in the installation directory.
All the schedules can then be managed by the MMC (Microsoft Management Console) Task Scheduler under the dedicated folder Seal Report.
Seal Report Scheduler
On Linux OS or Azure Platform, a dedicated Seal Report Scheduler may be used instead of the Windows Task Scheduler.
Schedule definitions are stored in the dedicated repository folder: \SpecialFolders\Schedules and are executed by either another process or an worker thread in the Web Report Server.
Windows Task Scheduler: Check users and synchronization
A Schedule is created by a Windows Users (the one running the Report Designer or the Web Report Server) but can be executed by another Windows User.Be sure that the Windows User has the rights to execute the report and process the output.
You can synchronize schedules from the Server Manager if reports have been moved/copied with the Windows Explorer.
Just run the Server Manager in Administrator mode and select the menu
Define alerts
Alert and regular checks can be easily implemented using a report and a schedule.Create a SQL Select statement that detects an anomaly in your database.
Just create a report output on an email address with the option
Cancel generation if no records and schedule it regularly (Every 15 minutes, the reports is executed, if a record is returned, an email will be sent.
Task Folder Name property.
System Reports for Schedules
Use dedicated schedule reports from the \Reports\System Repository sub-folder:- 320 Reports - Web Server Schedule Definitions (only valid if the Seal Report Scheduler is used)
- 360 Reports - Last Schedules Executions (only valid if the Audit database is enabled)
Tasks & ETL
A Report Task is a SQL or a Razor Script executed at a given step of the report execution.
A task references one Data Source and one Connection and is instanciated from a Task Template to define default scripts and parameters.
A report can have several tasks executed sequentially from the top to the bottom.
A task can have tasks children that are executed sequentially by the parent task.
A task can be executed at different steps of the report generation (
If a task is a Razor Script, it can stop the report execution by setting the report.Cancel flag to true.
Thus, simple workflows can be implemented with tasks (
Using the Execute for each connection property, a task can be executed for all connections defined in the Data Source.
As Tasks executes a Razor Script, they can reference, instantiate and use objects from any .Net/.NET Core Assemblies located in the \Assemblies Repository sub-folder.
ETL Tasks
Several Task Templates are dedicated to perform ETL operations: Loading an Excel Sheet to a database table, copying tables between databases, unzipping a file, download from FTP Server, etc.
The task templates Loop (to loop over a list of objects) or Parallel (to execute children simultaneously) allow to perform several taks in parallel (multi-threading).
Task Templates
Execute Report, File Download Upload, File Zip Unzip, Load Excel To Database, Load CSV To Database, Loop, Parallel, etc. are template files defined in /Sources/TaskTemplates Repository sub-folder.By default use the Default template.
Just add your own template in this folder.
Schedule your tasks
As tasks are part of the report, they can be scheduled as a normal report, even if the model has no element.In the tree view, right click on the Schedules node and select the menu Add Schedule for Report Tasks.
Tasks Samples
Check the Repository Samples from the \Reports\Samples\01-Tasks Repository sub-folder:- 101-Task Refresh Enumerated Lists
- 102-Task Generate several Report Results
- 103-Task Update Navigation Link Text
- 104-Task Add borders to result tables
ETL Tasks Samples
For ETL features, check the Repository Samples from the \Reports\Samples\06-ETL Tasks Repository sub-folder:- 601-Load Excel Files
- 602-Load CSV Files
- 603-Execute Reports
- 604-Copy Tables from a Database
- 605-Unzip Files
- 610-Download Zip from FTP, Unzip and Load tables from Excel
- 611-Generate Report Results, Zip and Upload to FTP Server
Input Values
To prompt a value to the user before executing the tasks or before executing a report, you can define Report Input Values (
This collection property is available in the root Views folder node of the main Tree View.
Like Common Value, the restriction will be prompted when the report is executed and the value can be used in the tasks or in other scripts used to generate the report result..
The value prompted can be either a text, a numeric, a date time or values of an enumerated list.
@using Seal.Model
@{
ReportTask task = Model;
Report report = task.Report;
foreach (ReportRestriction restr in report.InputValues) {
report.LogMessage("[{0}]={1} Value={2}", restr.DisplayNameEl, restr.DisplayText, restr.FirstValue); //You can use restr.Value1, restr.FinalDate1, restr.EnumValues[0], restr.EnumDisplayValue, restr.FirstStringValue, restr.FirstNumericValue, restr.FirstDateValue
}
}
Input Values Samples
Live Sample: 03-Input Values/300-Input Values - Connection and thresholdThis reports show the use of 2 input values.
Smart Copy
When using the Report Designer, the Smart Copy feature can be used to ease the report edition.
It allows the copy of property values from a source object to several destinations objects (
In addition, the Smart Copy can copy a source object to several destinations objects (
You can also use the Smart Copy when editing a report model: Just right click on a report element or restriction to show the popup menu.
Find and replace using Notepad
As all Seal Report files are XML, you can easily edit them with your favorite NotePad and use its find/replace features.Just save the file and reload the Report (or the Data Source) to check your modifications.
This may be also useful to copy MetaData, change Data Source GUID, etc.
Execution Steps
When a report is executed, the following process is done:
Step 1: Execute Report Tasks having step 'Before models generation'
Tasks are executed sequentially (SQL or C# Script) from the top to the bottom.
If a task has a razor script returning "0", the report is cancelled.
Step 2: Build Models
Models are grouped and executed sequentially using the Execution set property.
Models having the same Execution set are executed in parallel (one model per thread).
Step 2-1: For each model having a SQL Source:
-
Fill the model result table (DataTable)
Run the 'Pre Load Script' if any, generate the SQL statement, query the database to fill the result table (DataTable), run the 'Post Load Script' if any.
- Build the model pages: Create the pages (ResultPage) containing the page table (ResultTable) and data table (ResultTable)
- Create the model Summary Table (ResultTable).
- Process the totals in the result tables.
- Handle the 'Cell script' for each cell (ResultCell) in the Data tables and then in the Summary table.
- Calculate the series (this involves calls to 'Cell script' if any).
- Perform final sort.
- Execute any 'Final Script' defined in the models.
Step 2-2: For each model having a LINQ Source:
-
Fill the model result table (DataTable):
Init Sub-Models and Sub-Tables based on the model definition.
For each sub-model (which have always a SQL Data Source), build the result table (DataTable) as described in the step 2-1.
For each sub-table, build the result table (DataTable) definition using table source 'Definition Script' and load it using either the table source 'Default Load Script' or the model 'Load Script'.
Generate the LINQ query and execute it to fill the result table (DataTable) using result tables of the Sub-Models and the Sub-Tables. - Build the model pages: Create the pages (ResultPage) containing the page table (ResultTable) and data table (ResultTable)
- Create the model Summary Table (ResultTable).
- Process the totals in the result tables.
- Handle the 'Cell script' for each cell (ResultCell) in the Data tables and then in the Summary table.
- Calculate the series (this involves calls to 'Cell script' if any).
- Handle Sub-totals to add extra lines.
- Handle 'Empty if repeated' option to empty repeated values.
- Perform final sort.
- Execute any 'Final Script' defined in the models.
Step 3: Execute Report Tasks having step 'Models generated, before rendering'
Tasks execution as Step 1.
Step 4: Render Views
Sequentially render report views from the root Report View to generate the result (from top to bottom).
Step 5: Execute Report Tasks having step 'Rendering is done, before output execution'
Tasks execution as Step 1.
Step 6: Process Output
If any, process the output defined for the execution.
- Check if the 'Pre Execution Script' returns '0' or option to cancel if no records
- Execute the output on the selected Device
- Execute the 'Post Execution Script'
Step 7: Execute Report Tasks having step 'After execution'
Tasks execution as Step 1.
Contribute to Seal Report
Enhance the documentation and samples
Want to share your experience or to add a new topic ? Something is not clear in the documentation ? Do you have an interesting recipe ?As the site for the documentation is part of the solution, you are welcome to Pull a Request at GitHub.
Add translation files
Do you have a translation file not yet supported by Seal Report ?As the translations are part of the project, feel free to Pull a Request at GitHub.
Sponsor the project
If you are using Seal Report in a business application, please consider to sponsor the product to ensure its maintenance, quality and independence.Please check Support and Sponsor.
And more...
You are also welcome to help us in several different areas:- Beta testing.
- Libraries of Data Sources and Reports on standard databases.
- Additional View templates.
- New features development.